 7
7
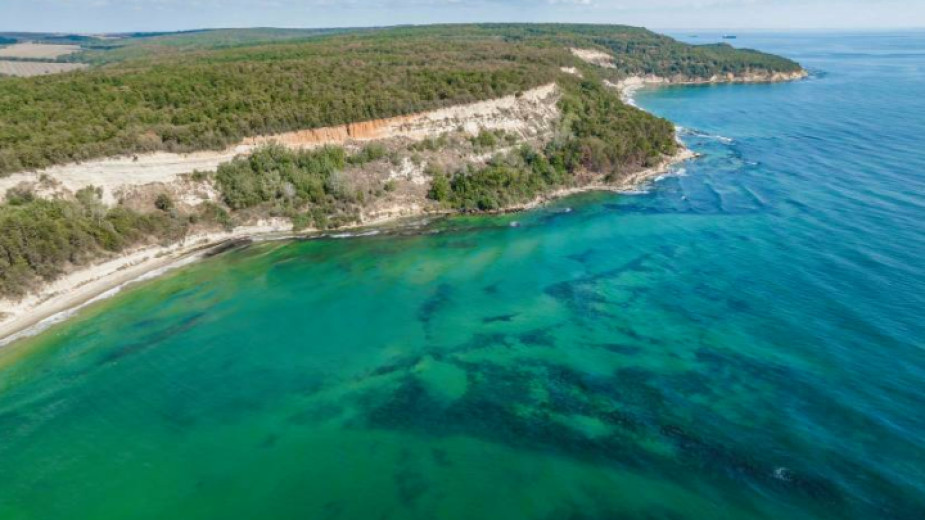
Exploration of the water between Cape Kilik and Ilanjik Point, north of the mouth of the Kamchia River, has revealed some unique discoveries. Once, ancient ships were sheltered in these secluded coves from the tempestuous waters of the Black Sea. It turns out that this part of the Bulgarian coastline is dotted with archaeological landmarks. These include mound necropolises, ancient settlements, etc. Nearby, remains of the Roman fortress and road station Erite were found.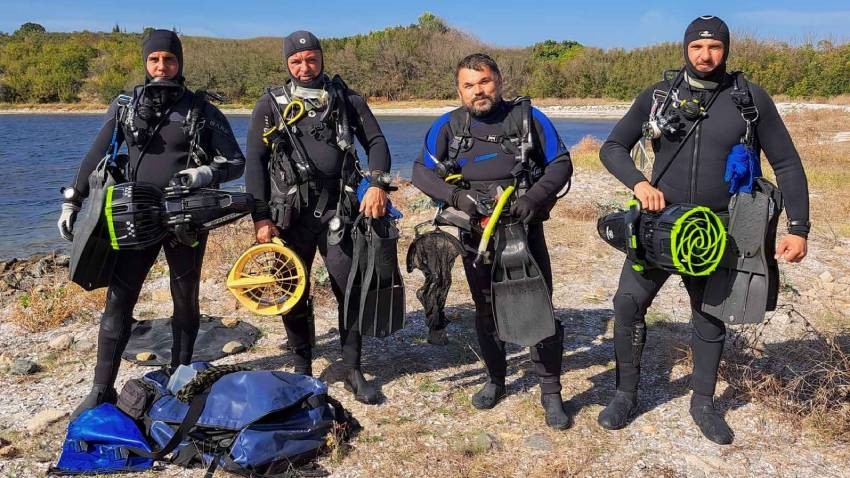
This autumn, a team of divers led by Professor Ivan Hristov, deputy director of the National History Museum, made a series of curious discoveries during a multidisciplinary underwater research expedition. The earliest find is an amphora dating from the 5th century BC, which was brought all the way from the island of Chios and has survived almost intact to the present day. And there is more:
"Next, we have some extremely interesting finds from the Roman period - says Prof. Ivan Hristov for Radio Bulgaria. - I was lucky enough to find a Roman tin ingot with a pure tin content of 98% in waters with very poor visibility. This is the first underwater find of its kind on the Bulgarian Black Sea coast and, frankly, I know of no similar find on land.
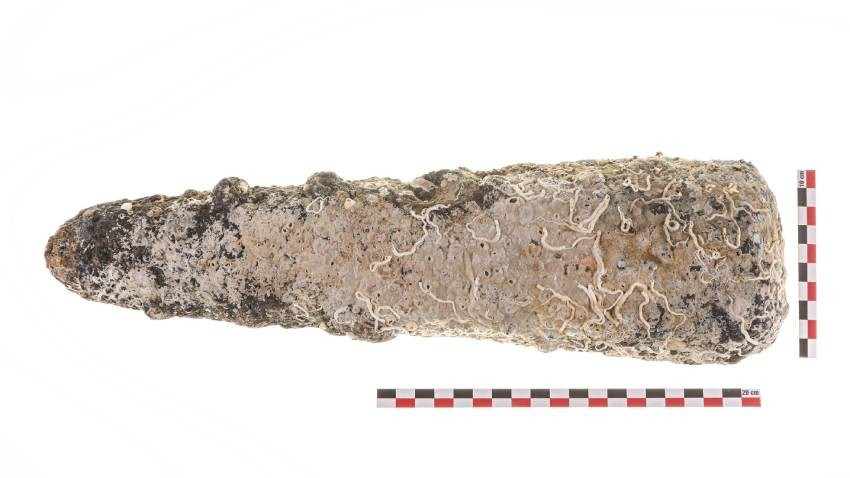

It weighs 5kg, 400g and its only rival is an ingot from Cornwell, England, found in a tin smelter. It is very likely that these are the same moulds that were used in ancient times to cast this rare and expensive raw material. Tin was used in the manufacture of bronze objects, including the minting of bronze coins. It was transported by ship to our country, more precisely to the Roman cities on the Black Sea coast.
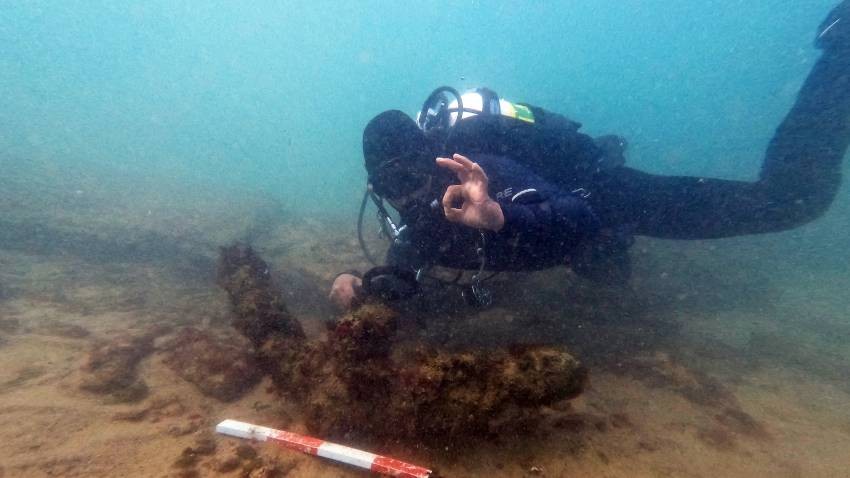
The archaeologists made another curious discovery - a stone perirrhanterion - an ancient Greek vessel used in pagan cults as a reservoir for holy water. It weighs 60kg and is almost intact. It was found in the shallows off Cape Killik. Which, it turns out, were dry land at the time.

"My hypothesis is that in ancient times there was a temple on this promontory - a sanctuary where the sea gods were worshipped - says Professor Hristov. Sailors who came to this cape, to this bay, would offer certain sacrifices. This hypothesis is supported by the discovery of half of a stone anchor for a classical wood and stone anchor. It had no practical function, but was a symbol, a gift from the sailors who sailed past this promontory".

In the tiny bay of Ilanjik, divers have found a sunken Ottoman-era ship with a well-preserved wooden keel. Could the ship have crashed into the shallows, which are difficult to see in a storm? At the mouth of the Kamchia River, geophysical surveys have identified the outline of a small island that has since been washed away.
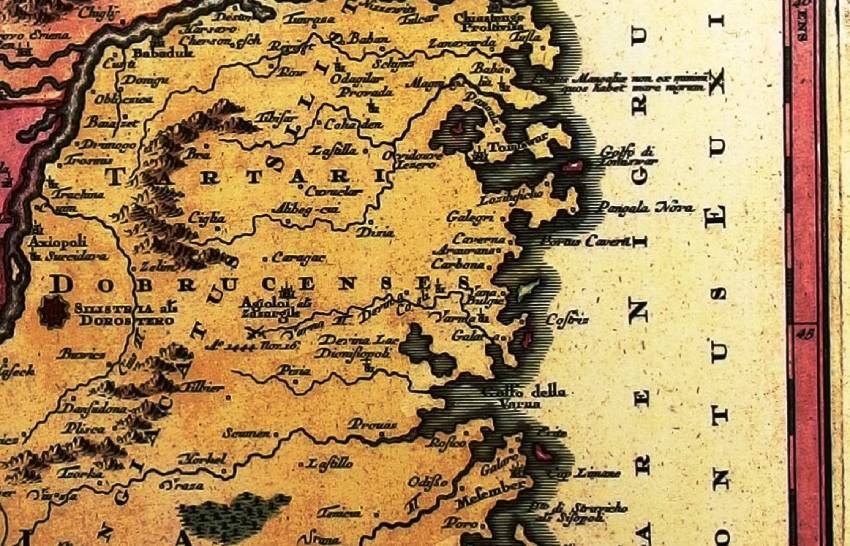 Interestingly, like other islands that no longer exist, it appears on many Western European maps from 1452 to 1750. According to specialists, the sea level of the Black Sea was lower in the Middle Ages. The coastline was different from today, there were smaller and larger islands. This is probably the case with the invisible island at the mouth of the Kamchia River, which the locals call the Kamchia Stone.
Interestingly, like other islands that no longer exist, it appears on many Western European maps from 1452 to 1750. According to specialists, the sea level of the Black Sea was lower in the Middle Ages. The coastline was different from today, there were smaller and larger islands. This is probably the case with the invisible island at the mouth of the Kamchia River, which the locals call the Kamchia Stone.

Further readings:
Photo courtesy of the National Museum of History
Translated and posted by Elizabeth RadkovaThere are rumours and speculations that some forgeries, so good that they are not inferior to the originals, could be found among the exhibits in the museums, but at the moment a whole series of forgeries can be seen at an exhibition..
A unique statue from the Roman period of Odessos, preliminarily dated to the late 2nd to the first half of the 3rd century, has been discovered during excavation works near the train station in Varna, said archaeologists from the Varna Regional..
Petrich municipality has received an award for original promotion of the tourist destination Heraclea Sintica , Katya Stoyanova, head of the "Restoration, conservation and socialization of Heraclea Sintica" project, said this for BTA. The award..
The head of the statue of Tyche, the goddess of Philippopolis, has been discovered in the Episcopal Basilica in Plovdiv, said the head of the..

+359 2 9336 661
