The National Archaeological Institute with Museum /NAIM/ at the Bulgarian Academy of Sciences has opened doors for its 11th annual National Archaeological Exhibition, named Bulgarian Archaeology 2017. Traditionally the exhibition displays the field work of Bulgarian archaeologists over the past year with the best findings and numerous photos. The exposition comes to mark the Day of Archaeologists, February 14th. A total of 340 exhibits from 22 sites and posters for 50 researches have been presented this time.
“This is perhaps one of the richest and most diverse exhibitions, seizing a period of the earliest pre-historic times, through the Middle and Late Paleolithic era and up to the Late Medieval Age,” says archaeologist Dr. Kamen Boyadzhiev during the traditional press conference prior to the event’s unveiling. Ceramic objects from the village of Damyanitsa, South-West Bulgaria can be seen, dated back to the 6th millennium BC. There are even older artifacts, but the Damyanitsa ones reveal the great artistic gift of those ancient craftsmen.
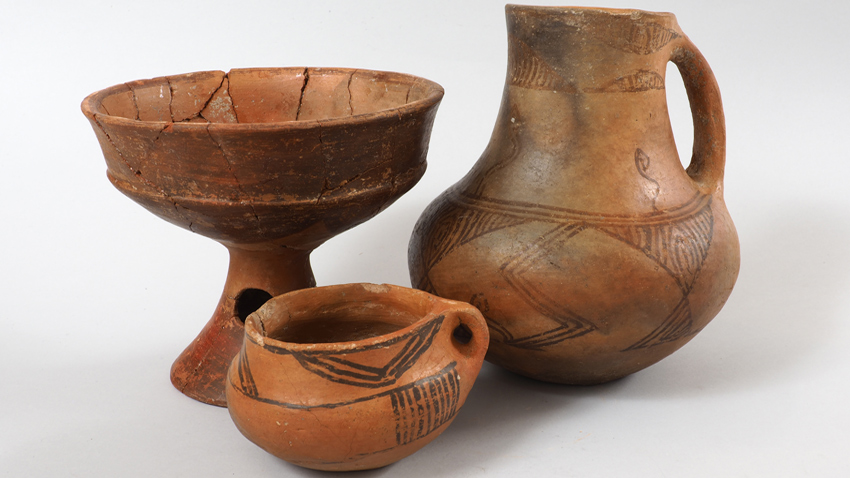

The great antique epochs continue to be well-presented. Ancient Greece is viewed through the well-preserved Apollonia Pontica town within what’s today Sozopol. There are numerous artifacts from the Roman Age, coming from Sofia, Plovdiv and the ancient Serdica and Philippopolis. In 2017 the accent of the discoveries was on Medieval Bulgaria – 10 - 14th c. BC.
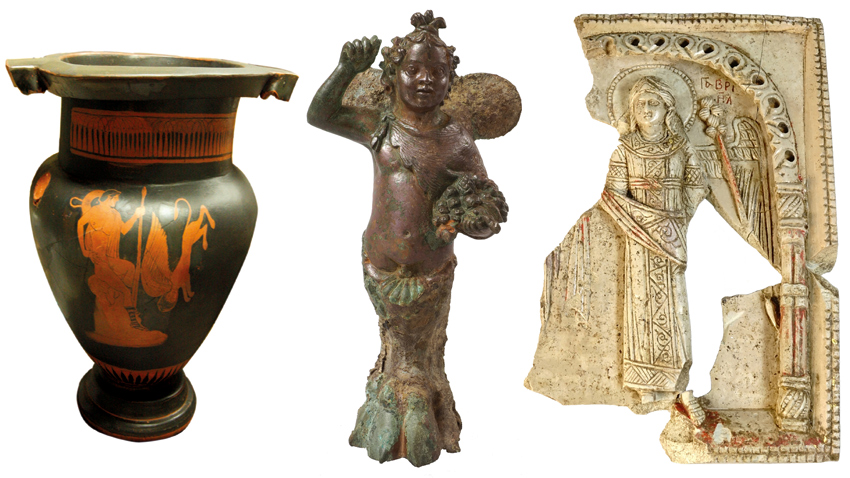

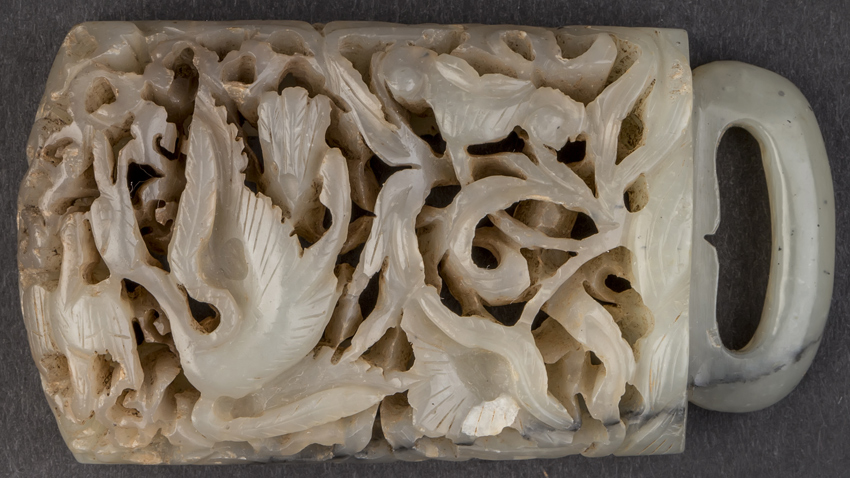
“There are things which I see for a first time so well-preserved, I must admit that,” Kamen Boyadzhiev comments. “For instance – a bronze flute from Debelt and a torch stand from Pliska. There are objects that are really interesting, but require a bit more attention, a more detailed look. Let’s take as an example this really rich collection of anthropomorphic clay figures from Damyanitsa, dated back to the 6th – 5th millennia BC. Then we have an icon from the Trapezitsa Hill in Veliko Tarnovo… The jade belt buckle from Cape Kaliakra is one of the most interesting artifacts, really impressing with its preciseness and also with the riddle of its origin – how did it reach what’s today Varna…?”

The buckle mentioned was made in China in the period of the Yuan Dynasty /1206 – 1368/, but the hunting motifs have strong Mongol influence. There is hypothesis that this type of belt buckles was used as part of a warrior’s funeral clothing, discovered across tombs of the Yuan Dynasty’s aristocratic representatives.
Kaliakra, where the buckle was discovered, used to be a medieval settlement within the Despotate of Dobrudja – a Bulgarian state spreading across North-East Bulgaria in the 14th c. The despotate had huge military and trade fleets and obviously had relations even with the Far East.
Head of the National Archaeological Institute with Museum at BAS Associate Prof. Dr. Lyudmil Vagalinski pointed at some serious problems of Bulgarian archaeology, also relevant for Europe. He was talking about the introduction of private associations within archaeological research. The acting legislation in this country says that state institutions deal with archeological activities, but there has been pressure for the introduction of other entities, mostly under the form of NGOs. According to Associate Prof. Vagalinski the change of the model and the introduction of private subjects, had its negative impact across a series of European countries. The problem could get even worse in Bulgaria due to the numerous treasure hunters:
“There is no other country in Europe with 30,000 acting treasure hunters, systematically working. This is what they do for a living, with high level dealers working internationally. I was told that by the respective services that had been trying to cope with them, but in my opinion those lack enough resource and in fact this hysteria is still out of control. I think that any demand on private subjects’ introduction might be dreadful for the archaeological heritage that we are so proud of.”
The next curious project of the National Archaeological Institute with Museum at BAS will be the Sports in Antique Thrace exhibition which will be unveiled on April 1st.
English version: Zhivko Stanchev
Photos: courtesy of NAIM
Archaeologists have explored a necropolis in the Kavatsi area near Sozopol. The perimeter in which it is located is part of the history of Apollonia Pontica and is dated to the 4th century BC. "This is a site with interesting burials in which a nuance..
On November 10, 1989, at a plenum of the Central Committee of the Bulgarian Communist Party, Todor Zhivkov was removed from the position of General Secretary - the highest position in the party and the state. What happened at the..
Archaeologists have discovered a very rare and valuable glass bottle in a 2nd-century tomb in the southern necropolis of the Roman colony Deultum near the village of Debelt (Southeastern Bulgaria). What makes it unique is that it depicts the myth of..
On November 25, the Bulgarian Orthodox Church honours the memory of St. Clement of Ohrid – a distinguished archbishop, teacher and scholar. He was among..

+359 2 9336 661
